hyperdynamic lv function LVH is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart becomes thick and stiff due to pressure overload. It can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain and heart failure. Learn about the . For free. Translate Daddy i need you. See Spanish-English translations with audio pronunciations, examples, and word-by-word explanations.
0 · left ventricular hypertrophy test results
1 · left ventricular hypertrophy lab tests
2 · left ventricular function becomes hyperdynamic
3 · is hyperdynamic left ventricle dangerous
4 · hyperdynamic lv function causes
5 · hyperdynamic left ventricular function guidelines
6 · hyperdynamic left ventricle stress test
7 · hyperdynamic left ventricle meaning
Looking for a specific product document? Our virtual resource center will help you find everything you need, including installation manuals, product brochures and more. Just click the proper section and check the download table. Select the document and it will download directly to your computer.
The LV is hyperdynamic to compensate for decreased preload from the RV. Based on clinical findings, including chest pain, shortness of breath, hypoxia, tachycardia, elevated BNP, troponin, and signs of right-sided heart failure on POCUS, a CT scan of the chest was .A hyperdynamic heart is defined as a left ventricular (LV) with an ejection fraction (EF) above the normal range. Is this favorable? We looked at the diastolic properties of subjects with a . I n heart failure (HF) patients, there is a well-known exponential relationship between left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) and mortality. However, the relationship of . Fourthly, the study suggested that patients with preserved LVEF between 50% and 60% or >65% had significantly higher mortality risk compared with the reference group. .
LVH is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart becomes thick and stiff due to pressure overload. It can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain and heart failure. Learn about the .
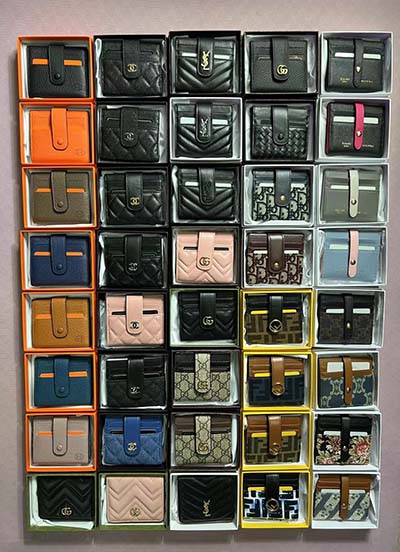
ysl wristlet
A hyperdynamic heart is defined as a left ventricular (LV) with an ejection fraction (EF) above the normal range. Is this favorable? We looked at the diastolic properties of subjects with a hyperdynamic heart and its impact on .The LV is hyperdynamic to compensate for decreased preload from the RV. Based on clinical findings, including chest pain, shortness of breath, hypoxia, tachycardia, elevated BNP, .
left ventricular hypertrophy test results
Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method to assess LV function. We also highlight the role of STE in the assessment and . Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork .
The heart may compensate by working harder to do its job. The extra work can lead to swelling or scar tissue buildup that affects the ventricle’s ability to fill and pump. You might not feel the effects of a slightly reduced ejection fraction. But as your heart function declines and your ejection fraction worsens, you can become severely ill. INTRODUCTION. While most patients with heart failure (HF), with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction, have low or normal cardiac output accompanied by elevated systemic vascular resistance, a minority of patients with HF present with a high-output state with low systemic vascular resistance. Tests may be done to check blood sugar, cholesterol levels, and liver and kidney function. Electrocardiogram. Also called an ECG or EKG, this quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. During an ECG, sensors called electrodes are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. Wires connect the sensors to a .
55 to 70% – Normal heart function. 40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure. Cardiac function is extremely variable in the setting of critical illness and depends on multiple physiologic determinants . Cardiac systolic function is related to heart rate, preload, afterload, and contractility. A patient’s EF may be hyperdynamic in the setting of critical illness owing to changes in these basic physiologic parameters. A hyperdynamic heart is defined as a left ventricular (LV) with an ejection fraction (EF) above the normal range. Is this favorable? We looked at the diastolic properties of subjects with a hyperdynamic heart and its impact on outcome. Consecutive echocardiography examinations during 5 years were ev . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) is calculated as the difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and .
Video: La fracción de eyección del corazón. What is “ejection fraction”? Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction.
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. In response to this pressure overload, the inner walls of the heart may respond by getting thicker.
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy. The following are key points to remember about this article on assessing left ventricular (LV) systolic function: from ejection fraction (EF) to strain analysis: LVEF, defined as the ratio of LV stroke volume to LV end-diastolic volume, is one of the most frequently measured variables in clinical practice. However, LVEF is an imperfect measure . Hyperdynamic LV systolic function can be attributed to underresuscitation, severe vasoplegia, or sympathetic overstimulation. 24, 25 The noninvasive markers of preload (E/e’ (ratio between early mitral inflow velocity . Normal LV diastolic function requires integration of left ventricular ejection, relaxation, and structure and is an active energy-requiring process. 1 For example, LV diastolic function becomes markedly abnormal immediately following coronary ligation, before detectable changes in other measures of cardiac function, including wall motion or electrocardiographic .
Hyperdynamic LV function is defined as near or complete obliteration of the LV cavity, meaning that the endocardial surfaces of the LV free wall and septum come in close contact with each other. From: Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia, 2019. About this page. Add to Mendeley Set alert.
left ventricular hypertrophy lab tests
The LV systolic function is hyperdynamic by eyeball semi-quantitative estimation in this clip. There is significant reduction in LV cavity size during systole. In addition, the anterior mitral valve leaflet contacts the septum in early diastole (EPSS). The mitral annular excursion appears normal.
Hyperdynamic LV systolic function was defined using LV ejection fraction (LVEF) of 70% as cutoff. Secondary outcomes were heart rate, LV end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), and E/e' ratio. Results: Four studies were included, and the pooled prevalence of hyperdynamic LV systolic function was 18.2% ([95% confidence interval (CI) 12.5, 25.8]; I 2 = 7 . Patients with BD from young adulthood are likely to have LVH with normal LV function and hyperdynamic heart associated with diastolic dysfunction. Low-grade inflammation may underlie the mechanisms of LV hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction in BD patients. Diastolic dysfunction – Impaired LV relaxation is common in patients with HCM and can be a cause of symptoms. In patients with HCM, noninvasive measures of diastolic function are generally considered unreliable. Ventricular arrhythmias – In patients with obstructive HCM, ventricular arrhythmias are a rare cause of exertional symptoms .
handyhülle gucci
Consequently, most obese individuals have normal or hyperdynamic left ventricular systolic function. 3 Diastolic dysfunction may be detectable in as many as 57% of obese individuals (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m 2) aged >50 years 4; the proportion of obese individuals with systolic dysfunction is less clear, and the proposition of an .
left ventricular function becomes hyperdynamic
dolce and gabbana crystal shoes
Dacia Jogger ir pieejams ar 5 vai 7 ērtiem sēdekļiem un piedāvā perfektu komforta un daudzpusības apvienojumu! Plānojiet savus braucienus tā, kā jums ērtāk, un izmantojiet plašās salona konfigurēšanas iespējas. Izbaudiet komfortu, ceļojot kopā ar ģimeni vai draugiem, pateicoties 7 ērtām sēdvietām.
hyperdynamic lv function|hyperdynamic left ventricle stress test