lv strain adalah References. Sovari AA, Farokhi F, Kocheril AG. Inverted U wave, a specific .
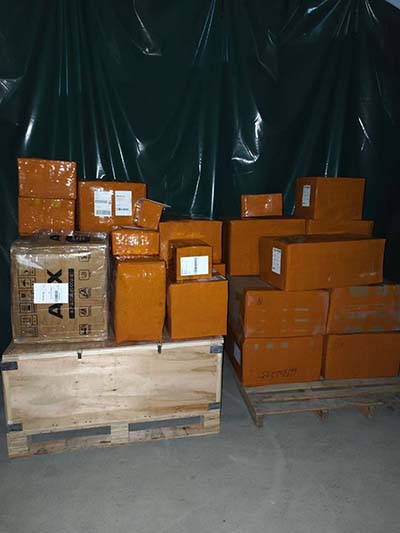
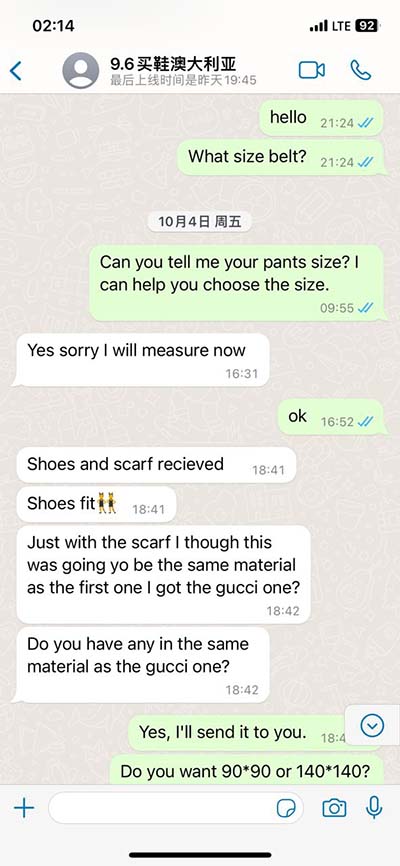
Description: NAME: LOUIS VUITTON Monogram Savannah Chapman Brothers reversible belt SHAPE: belt MODEL NO.: MP010T Code: BC5106 COLOR: WhitexNavy MATERIAL: Monogram Savannah Canvas APPROX SIZE: Total Length: 42.7inch / 108.5cm Band Width: 1.5inch / 3.8cm Waist Length: 34.3 - 38.2inch / 87cm ~ 97cm Holes: 5 Size .
0 · lvh strain pattern
1 · left ventricular strain
S$ 1,080.00. Call for Enquiry. Belts. LOUIS VUITTON Official site - LV Heritage 35mm Reversible Belt is exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton Stores. Discover more of our Accessories Men's Belts Collection by Louis Vuitton.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST .
RWPT in wide QRS complex tachycardia. R-wave peak time (RWPT) may be .
Right ventricular strain pattern = ST depression / T wave inversion in the .ECG Criteria for Left Atrial Enlargement. LAE produces a broad, bifid P wave in .In LBBB, conduction delay means that impulses travel first via the right bundle .References. Sovari AA, Farokhi F, Kocheril AG. Inverted U wave, a specific .
lvh strain pattern
Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°.. Normal Axis = QRS axis between .
Hipertrofi ventrikel kiri atau left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) adalah suatu kondisi saat bilik atau ventrikel jantung bagian kiri mengalami pembesaran. LVH dapat terjadi karena bilik jantung merespons tekanan darah .Strain imaging that uses speckle tracking in 2-D and 3-D offers promise for quantifying LV function, particularly for patients with borderline LV function, because of the potential to identify subclinical disease.
This article reviews the definition of left ventricular strain, outlines the types of strain and reviews how strain is acquired and measured. In addition, the advantages of strain analysis over LVEF as well as the incremental prognostic .This article reviews the definition of left ventricular strain, outlines the types of strain and reviews how strain is acquired and measured. In addition, the advantages of strain analysis over LVEF .
left ventricular strain
LVEF, defined as the ratio of LV stroke volume to LV end-diastolic volume, is one of the most frequently measured variables in clinical practice. However, LVEF is an .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a .ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and . Left Ventricular Hypertrophy or LVH is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Learn symptoms and more. Peak strain is the maximum strain, whereas the peak systolic strain is the maximum strain that occurs specifically during the LV ejection period (i.e. before aortic valve closure). Post-systolic thickening, and the post .
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork .adalah pola EKG klasik BVH, paling sering terlihat pada anak-anak dengan Ventricullar Septal defect (VSD). Cara Mudah Belajar EKG dan Aplikasinya Bayu Budi L 99 Katz . LVH: (S V2 + R V5 = 35 mm, R aVL > 11 mm) disertai tanda LV strain (T- inversion in V4-6).
In the arrhythmia group, the LV global peak radial strain and global peak circumferential strain values of real-time TPAT were significantly different from those of the conventional technique . BACKGROUND: Imaging evaluation of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) remains challenging. Myocardial strain assessment by echocardiography is an increasingly utilized technique for detecting subclinical left ventricular (LV) and right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic .
Speckle tracking echocardiography permits assessment of myocardial strain in three spatial directions (longitudinal, radial and circumferential) independent of the angle of insonation of the ultrasound beam. Longitudinal strain is probably the most frequent type of strain used to characterise LV systolic function in clinical practice.
Compared to patients without ECG strain, patients with ECG strain had more severe AS, higher LV mass index, high troponin I levels, and more diffuse fibrosis by CMR. All patients with ECG strain had mid-wall late gadolinium enhancement, which was independently associated with ECG strain. ECG strain was an independent predictor of aortic valve .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. This is more than what is usually seen with pure LV "strain". Note how the inverted T waves look symmetric in V4-thru-V6 - with much sharper descent than the usuallly more gradual ST decline (seen in Figure 3 in the above LVH link). In addition - the upright T wave in lead V3 is quite peaked. This is not the reciprocal of pure "strain". Electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) has many faces with countless features. Beyond the classic measures of LVH, including QRS voltage and duration, the left ventricular (LV) strain pattern is an element whereby characteristic R-ST depression is followed by a concave ST segment that ends in an asymmetrically inverted T wave.

Even though 3D LV strain assessment is not complicated and provides much more information from the single acquisition than two‐dimensional (2D) evaluation, it requires special echocardiographic equipment, which is not widely available and inexpensive. This is raising the question about cost‐effectiveness of 3D echocardiographic assessment .Hipertrofi ventrikel kiri adalah pembesaran bilik (ventrikel) kiri jantung. Pembesaran bilik kiri jantung ini biasanya disebabkan oleh tekanan darah tinggi atau hipertensi. Bilik atau ventrikel kiri jantung merupakan pelabuhan terakhir bagi darah yang kaya oksigen sebelum meninggalkan jantung. Ventrikel kiri jantung akan memompa darah ke .of LV strain measured by MRI from studies of healthy patients and to determine whether patient and MRI factors influence LV strain Key Finding For left ventricular (LV) strain MRI measurements, low-er limits of normal (LLNs) and 95% CIs were less affect-ed than mean values by patient and MRI factors. LLN When performing an echocardiogram, the use of global longitudinal strain to help detect subclinical LV dysfunction is endorsed by the 2014 expert consensus for multimodality imaging by the ASE and EACVI as well as the ASCO guidelines. 4,6 Subclinical LV dysfunction is defined by a relative decrease in the absolute value of strain by more than .

Conclusions: In patients after Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) with LV GLS >-13,8% had less in functional capacity and in 6 MWT distance compared with LV GLS < -13.8%. The 6 MWT . LVH: Voltage criteria for LVH (S V2 + R V5 = 35 mm, R aVL > 11 mm) with signs of LV strain (T-wave inversion in V4-6). Persistent S waves in V5-6 suggestive of associated RVH. Example 2. Biventricular hypertrophy. .
Left Ventricular Strain (LV Strain) LVH sering berhubungan dengan depresi segmen ST dan inversi dalam dari gelombang T. Perubahanini tampak di sadapan prekordial, V5 dan V6. pada sadapan ekstrimitas terdapat .
Furthermore, LV strain is partly load-dependent, but significantly less than E/A or E/e’. Low intra- and interobserver variability gave advantage to LV longitudinal strain over LV ejection fraction, “the holy grail” parameter of LV systolic function, and recommended it for the evaluation and follow-up of LV function in large spectrum of The following are key points to remember about this article on assessing left ventricular (LV) systolic function: from ejection fraction (EF) to strain analysis: LVEF, defined as the ratio of LV stroke volume to LV end-diastolic volume, is one of the most frequently measured variables in clinical practice. There is ST-T wave depression in inferior and lateral leads consistent with ischemia and/or LV “strain”, if not other cause. There is 1-2 mm of ST elevation in lead aVR. U waves are seen in V2,V3 — and possibly also in V5,V6 (fusing with the terminal portion of the T wave in these leads). We are not given any prior tracing for comparison .
Bouthoorn S, et al. (2018). The prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in men and women with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review . Background— The extent of viable myocardial tissue is recognized as a major determinant of recovery of left ventricular (LV) function after myocardial infarction. In the current study, the role of global LV strain assessed with novel automated function imaging (AFI) to predict functional recovery after acute infarction was evaluated. Methods and Results— A total .
To quantify the global and regional left ventricular (LV) myocardial strain in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) tissue-tracking techniques and to .
Left ventricular hypertrophy itself doesn't cause symptoms. But symptoms may occur as the strain on the heart worsens. They may include: Shortness of breath, especially while lying down. Swelling of the legs. Chest pain, often when exercising. Sensation of rapid, fluttering or pounding heartbeats, called palpitations. BackgroundBoth ECG strain pattern and QRS measured left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy criteria are associated with LV hypertrophy and have been used for risk stratification. However, the independent predictive value of ECG strain in apparently healthy individuals in predicting mortality and adverse cardiovascular events is unclear. Methods and ResultsMESA . Left ventricular (LV) systolic wall strain is a new candidate for prognostic indicator of hypertensive heart failure. It remains unclear how underlying transmural structural remodeling corresponds to LV wall systolic deformation as hypertensive hypertrophy progresses. We fed 68 Dahl salt–sensitive rats a high-salt (hypertensive group) or low-salt diet (control group) from 6 . Background Data on the prognostic value of left ventricular (LV) morphological and functional parameters including LV rotation in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) are currently scarce. In this study, we assessed the prognostic value of global longitudinal strain (GLS), global circumferential strain (GCS), .
A chic addition to the Heritage range, this LV Heritage 35mm Reversible Belt is available in three handsome colorways and elevated with three differently crafted finishes on the LV buckle, which is either brushed, hammered or striped.
lv strain adalah|left ventricular strain