lv normal size Taking the example of LV dimensions: just as 2.3% of normal individuals will have an LV size above the upper reference limit, a tiny proportion of normal individuals (just 0.15% of the . More than a simple open-air museum, the Village historique acadien is a tourism complex built around a 2.2 km circuit bordered with historic buildings, all inhabited by fully bilingual (French and English) interpretive guides who portray the daily lives of the Acadian people from 1770 to 1949.
0 · normal lv size and function
1 · normal lv end diastolic diameter
2 · normal lv dimensions
3 · normal lv diameter
4 · lv wall thickness normal values
5 · left ventricular wall thickness chart
6 · left ventricular diameter chart
7 · left ventricle size chart
Prises électriques et adaptateurs à Malte. A Malte, les prises électriques sont de type G. 🔌 . Vous aurez donc besoin d’un adaptateur pour pouvoir brancher et recharger vos appareils lors de votre voyage. Acheter un adaptateur pour Malte
∗ LV size applied only to chronic lesions. Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2 , maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , maximal LA volume ≤ . Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) .Taking the example of LV dimensions: just as 2.3% of normal individuals will have an LV size above the upper reference limit, a tiny proportion of normal individuals (just 0.15% of the .
tommy hilfiger? pe| tienda online oficial
Classifying LV size. Defining normal values for ventricular size is important for the standardisation of echocardiographic reporting, but is not a straightforward task. Normal and abnormal ranges depend on a number of factors including . Left ventricular (LV) diameter is routinely measured on the echocardiogram but has not been jointly evaluated with the ejection fraction (EF) for risk stratification of sudden cardiac death (SCD). Methods and Results.
Mean normal values for indexed end-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, and LVEF in men and women were 70 ± 15 and 65 ± 12 mL/m 2, 28 ± 7 and 25 ± 6 mL/m 2, and 60 ± 5% and 62 ± 5%, respectively. Men had larger .LV size was categorized by using either LV end-diastolic or end-systolic diameter or a qualitative assessment, as follows: normal, smaller than 4 cm; mildly enlarged, 4.1 to 5.4 cm .Radiopaedia.org, the peer-reviewed collaborative radiology resource
Table 26 Normal left ventricular myocardial thickness (in mm) in the adult measured on short axis images for men and women. Full size table. . Two studies were identified presenting normal values of the size of the pulmonary arteries in . The majority of these studies were focused on left ventricular (LV) cavity size, 3 . Serial long-term assessment of the natural history of asymptomatic patients with chronic aortic regurgitation and normal left ventricular systolic function. Circulation. 1991;84:1625–1635. Crossref. PubMed.
Figure 1. Calculation of left ventricular mass. mass LV = 1.05 (mass total – mass cavity) LV = left ventricle; 1.05 = mycoardial mass constant. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) A diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy is based on .Measurement of the size of the ventricle should be a part of every echo report, because it provides diagnostic clues and prognostic information, and enables the clinician to follow patients in respect of disease progression (or improvement). . The following table shows the normal dimensions of the ventricle as measured by the MMode. Normal .LV size was categorized by using either LV end-diastolic or end-systolic diameter or a qualitative assessment, as follows: normal, smaller than 4 cm; mildly enlarged, 4.1 to 5.4 cm moderately enlarged, 5.5 to 6.5 cm; and severely enlarged, larger than 6.5 cm.LV and LA can be within the ‘‘normal’’ range for patients with acute severe MR or with chronic severe MR who have small body size, particularly women, or with small LV size preceding the occurrence of MR.
A cornerstone of echocardiography is to ensure that normal reference intervals are available against which individual patients can be compared. Historical reference intervals have often been derived from studies or echo databases that included relatively small numbers of patients. . Changes in the reference intervals for LV ejection fraction . Background: Echocardiography remains the most widely used modality to assess left ventricular (LV) chamber size and function. Currently this assessment is most frequently performed using two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography. However, three-dimensional (3D) echocardiography has been shown to be more accurate and reproducible than 2D .
Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2, maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). ∗∗ In the absence of other etiologies of LV and LA dilatation and acute MR.
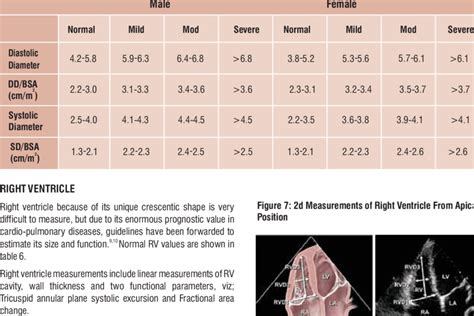
2. Echocardiographic Normal Ranges Meta-Analysis of the Left Heart Collab-oration. Ethnic-specific normative reference values for echocardiographic LA and LV size, LV mass, and systolic function: the EchoNoRMAL study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8:656–665. 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.02.014 3. One year later, another MRI study (lower image) was performed on the same patient and revealed an enlargement of left ventricular size with LVEDV of 314 ml, LVESV of 241 ml and a weakening of the heart function and ejection fraction EF of 23%. . *Resting Left Ventricle size Normal . *Peak Stress Left Ventricle Size Normal . *Right Ventricle .Normal thickness of the left ventricular myocardium is from 0.6 to 1.1 cm (as measured at the very end of diastole). If the myocardium is more than 1.1 cm thick, the diagnosis of LVH can be made. The left ventricular free wall is thickest at the base and it gradually thins towards the apex. At the tip of the apex myocardium is 1–2 mm thick,
Left ventricular hypertrophy also may be caused by gene changes that affect the heart muscle's structure. Things that can cause the heart to work harder and may possibly lead to left ventricular hypertrophy include: High blood pressure. Also called hypertension, this is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.1. Measurement of LV Size 3 1.1. Linear Measure-ments 3 1.2. Volumetric Measure-ments 3 1.3. Normal Reference Values for 2DE 6 1.4. Normal Reference Values for 3DE 6 Recommendation 6 2. LV Global Systolic Func-tion 6 2.1. Fractional Short-ening 6 2.2. EF 7 2.3. Global Longitudinal Strain (GLS) 7 2.4. Normal Reference Values 7 Recommendations 10 .
Echocardiographic Normal Ranges Meta-Analysis of the Left Heart Collaboration. Ethnic-specific normative reference values for echocardiographic LA and LV size, LV mass, and systolic function: the .1. Measurement of LV Size 3 1.1. Linear Measure-ments 3 1.2. Volumetric Measure-ments 3 1.3. Normal Reference Values for 2DE 6 1.4. Normal Reference Values for 3DE 6 Recommendation 6 2. LV Global Systolic Func-tion 6 2.1. Fractional Short-ening 6 2.2. EF 7 2.3. Global Longitudinal Strain (GLS) 7 2.4. Normal Reference Values 7 Recommendations 10 .(16%) had an indexed volume in the normal range. When LV size was defined more simply as normal or dilated by the same criteria, there was similarly poor agreement in classification (table 5). Of 692 patients with a dilated indexed LV volume, 346 (50%) had an LV diameter in the normal range, and 502 (73%) had a normal indexed LV diameter.
and the LVIDD was obtained using the standard M mode. LV size index was calculated as the LVIDD normalized for body surface area. Severe LV dysfunction was defined as EF ≤35%. The American Society of Echocardiography criteria were used to categorize subjects based on LVIDD.13 These criteria classify the LV size as normal (men: 42 to 59 mm .
The purpose of this study was therefore to establish normal ranges of LV volume and mass for the radial long-axis orientation. Materials and methods: Forty normal subjects (20 males, average age 32.3, age range 19-58; 20 females, average age 37.4, age range 21-54) were examined utilising a steady state free precession (SSFP) pulse sequence. Two .Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been a key variable for the diagnosis and management of heart failure over the last three decades. The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for assessment of cardiac dimensions and function.1 They describe four categories of left ventricular function and a ‘normal’ LVEF is .
Both low and low normal LVEF were independently associated with increased risk for incident CHF in our univariable and multivariable models (Figure 1 and Table 2).Compared with normal LVEF (reference group), low normal LVEF as associated with incident CHF in unadjusted [HR (95%CI): 3.58(1.74-7.33)], after adjusting for age, sex and race/ethnicity [HR . Background—Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. Methods and Results—End .Furthermore, in patients with degenerative mitral regurgitation who have normal LV size and systolic function, Magne et al 52 reported a 14% increase in the risk of adverse cardiac events for every 1% decrease in 2-D GLS. . Baseline echocardiogram shows normal left ventricular strain (2-dimensional global longitudinal strain). B, Reduced .A total of 1,589 subjects (feasibility 70%) had adequate LV data sets for analysis. Mean normal values for indexed end-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, and LVEF in men and women were 70 ± 15 and 65 ± 12 mL/m 2, 28 ± 7 and 25 ± 6 mL/m 2, and 60 ± 5% and 62 ± 5%, respectively.Men had larger LV volumes and lower LVEFs than women.
Quantitative assessments were derived from echocardiogram-based measurements. LV size was classified as follows: normal, smaller than 4 cm, mildly enlarged, 4.1 to 5.4 cm; moderately enlarged, 5.5 to 6.5 cm; and severely enlarged, larger than 6.5 cm. Patients in the preserved LVEF group were assumed to have normal LV size.
normal lv size and function
$19.89
lv normal size|left ventricular wall thickness chart